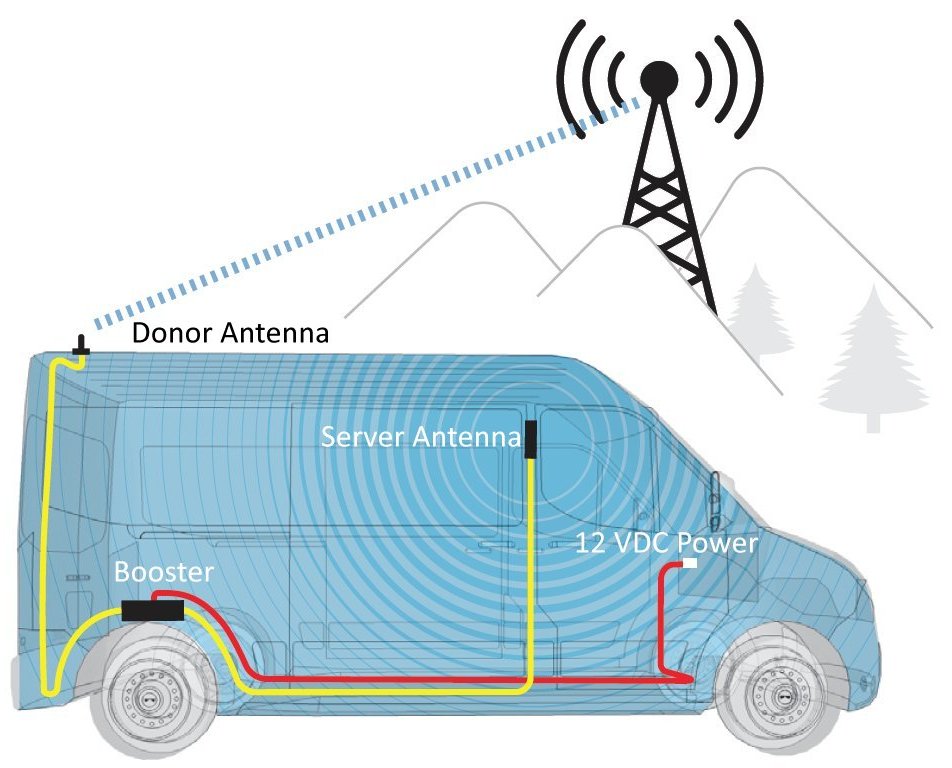
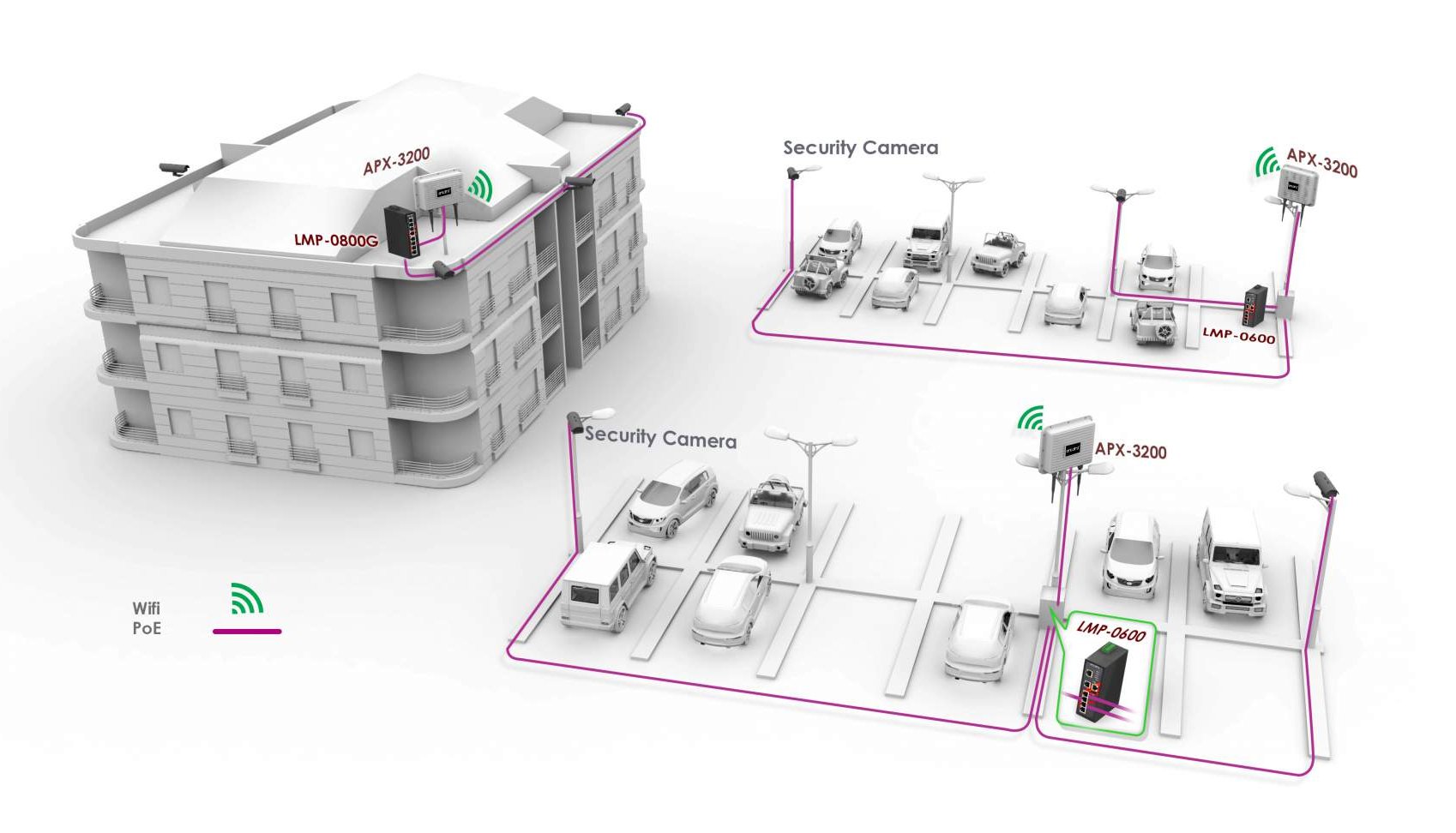
At this point, most IT pros and network engineers do not need to be convinced of the value of the Internet of Things (IoT). Instead, the focus is on finding practical ways to implement the technology. With explosive levels of adoption, there are many options out there. Some manufacturers are simply rolling Wi-Fi into everything. While this can work, it’s not economical over long ranges. The obvious alternative is to use LTE. Although, LTE data plans can get pricey. In the end, managing IoT over long distance amplifies the standard problems of large networks. Technologies used to connect IoT devices are commonly called Low-Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN). LPWAN may implement legacy cellular technology or direct radio communication. Continue reading…